SMILE™矫正中高度近视术后7年角膜后表面高度观察
作者:周行涛 等
通讯单位:复旦大学附属眼耳鼻喉科医院
发表杂志:J Cataract Refract Surg.
Chen Z, Zhao Y, Zhou X, Xia F, Zhao J, Zhou X. Seven-year observation of posterior corneal elevation after small incision lenticule extraction (SMILE) in patients with moderate and high myopia. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2021 Mar 9. doi: 10.1097/j.jcrs.0000000000000639. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 33770391.
背景:
角膜后表面高度被认为是评估屈光术后角膜稳定性的关键指标。增高的后表面高度值可能表明有早期角膜膨隆,因此,对于该高度值的长期观察可以帮助评估屈光术式的安全和稳定性。通过随访时间最长的关于SMILE™术后角膜后表面高度的临床观察,本研究再次证明SMILE™手术的长期安全稳定有效。
摘要
目的
研究SMILE™矫正中高度近视术后长期的角膜后表面高度变化。
设计
前瞻性病例系列研究。
方法
共计纳入接受SMILE™手术20例患者的33眼(患者30.1±9.5岁,7名男性,13名女性,术前等效球镜度[SE]范围为-4.00至-8.75 D,平均SE -6.25±1.29 D)。在术后7年的随访中,用Pentacam评估角膜后表面在中央(PCE),最薄点(PTE),最高点(PME),及其它在4毫米最佳拟合圆范围内的20个点的高度值。使用混合线性模型测量其变化,P <.05视为有统计学意义。此外,也评估高度变化与剩余基质厚度的相关性。
结果
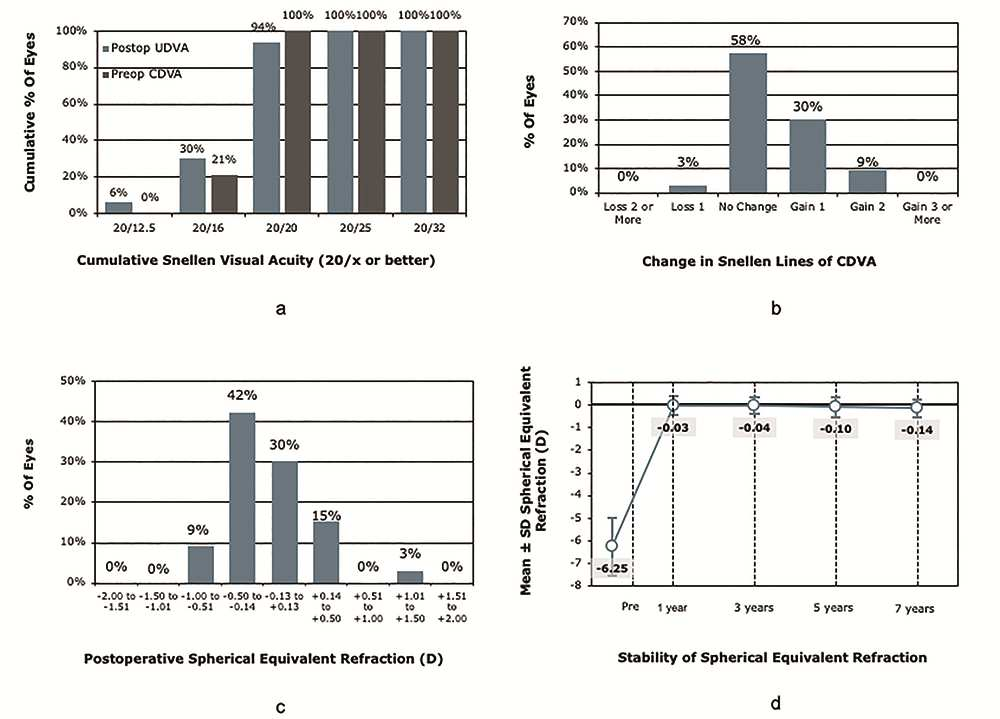
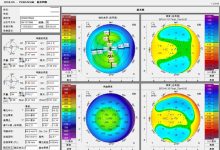
▲SMILE™术后7年随访的屈光结果。a)裸眼视力;b)最佳矫正视力的变化;c)等效球镜度;d)屈光稳定性。
所有33眼均未出现角膜膨隆。安全性指数1.08,有效性指数1.03。
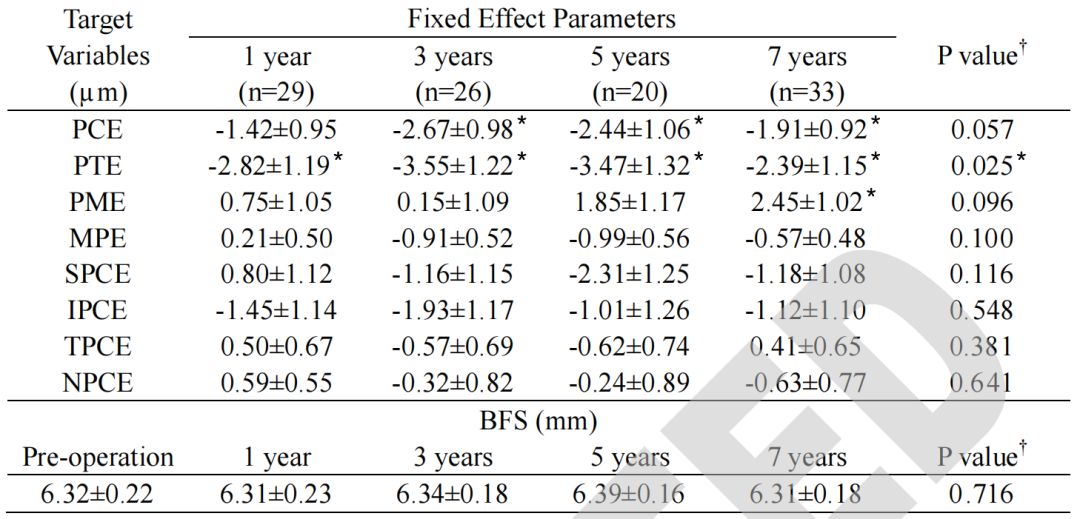
▲SMILE™术后角膜后表面高度相较基线值的变化。
PCE:后表面中央高度;PTE:后表面最薄点高度;PME:后表面最高点高度;MPE:后表面平均高度;SPCE, IPCE, TPCE, NPCE分别代表上、下、颞、鼻侧后表面高度;BFS:最佳拟合圆。
”*”: p <.05,差异有统计学意义。
PCT在术后1,3,5和7年的平均变化分别为-1.42±0.95, -2.67±0.98, -2.44±1.06和-1.91±0.92 μm. 其中,术后3,5,和7年的改变量有统计学意义(p分别为0.007, 0.023, 0.040)。PTE较基线值的改变量在术后各时间点均有统计学意义。其平均变化分别为-2.82±1.19, -3.55±1.22, -3.47±1.32, 和-2.39±1.15 μm (P分别为0.019, 0.004, 0.010, 和0.039). 术后7年,PME相较基线值的改变量为2.45±1.02。
PCT和PME的变化与剩余基质厚度呈负相关。
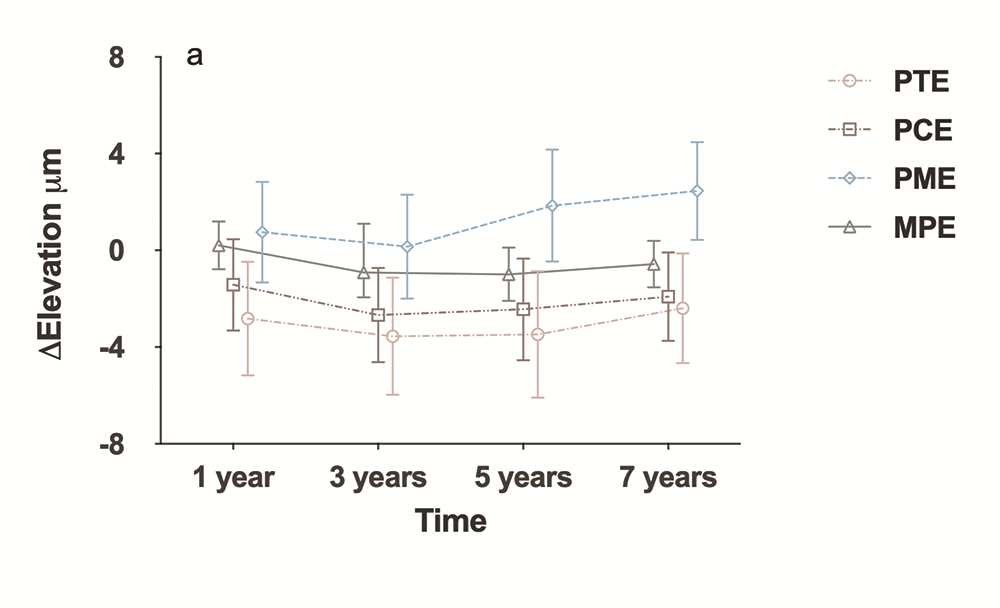
▲所有患者的角膜后表面高度变化(平均值和95%置信区间):PTE后表面中央高度;PME后表面最高点高度;MPE后表面平均高度;PTE后表面最薄点高度。
结论
SMILE™矫正中高度近视术后的角膜后表面高度长期稳定。
Seven-year observation of posterior corneal elevation after small incision lenticule extraction (SMILE™) in patients with moderate and high myopia
Zhuoyi Chen, Xingtao Zhou et al.
Abstract
Purpose
To investigate the long-term changes in posterior corneal elevation in moderate and high myopia after small incision lenticule extraction (SMILE™).
Setting
Eye & ENT Hospital, Fudan University.
Design
Prospective case series.
Methods
Thirty-three eyes of 20 patients (30.1+/-9.5 years, 7 male and 13 female, spherical equivalent [SE] range -4.00 to -8.75 D, average SE -6.25+/-1.29 D) who underwent SMILE™ were included. Changes in the posterior corneal elevation at central points (PCE), the thinnest point (PTE), the maximal point (PME), and an additional 20 points within the 4-mm area of the best-fit sphere were evaluated with a Pentacam (Oculus Optikgerate GmbH, Wetzlar, Germany) during a 7-year follow-up period. Mixed linear models were used to evaluate changes with P-values <0.05. Correlations of elevation changes and residual bed thickness (RBT) were also evaluated.
Results
No ectasia was observed among the 33 eyes. The safety index was 1.08, and the efficacy index was 1.03. The mean change in PCE at 1, 3, 5, and 7 years was -1.42+/-0.95, -2.67+/-0.98, -2.44+/-1.06, and -1.91+/-0.92 [micro]m, respectively. Significant differences were found at 3, 5, and 7 years (P=0.007, 0.023, and 0.040, respectively). PTE was significantly reduced at each time point compared to baseline. The mean change was -2.82+/-1.19, -3.55+/-1.22, -3.47+/-1.32, and -2.39+/-1.15 [micro]m, respectively (P=0.019, 0.004, 0.010, and 0.039, respectively). PME changed 2.45+/-1.02 [micro]m at 7 years compared to baseline (P=0.017). The changes in PCE and PME negatively correlated with the RBT.
Conclusions
Long-term posterior corneal elevation was stable in moderate and high myopia after SMILE™.
本篇文章来源于微信公众号: SMILE屈光天地


























 全飞秒
全飞秒 半飞秒
半飞秒 圆锥角膜
圆锥角膜 学术速递
学术速递

